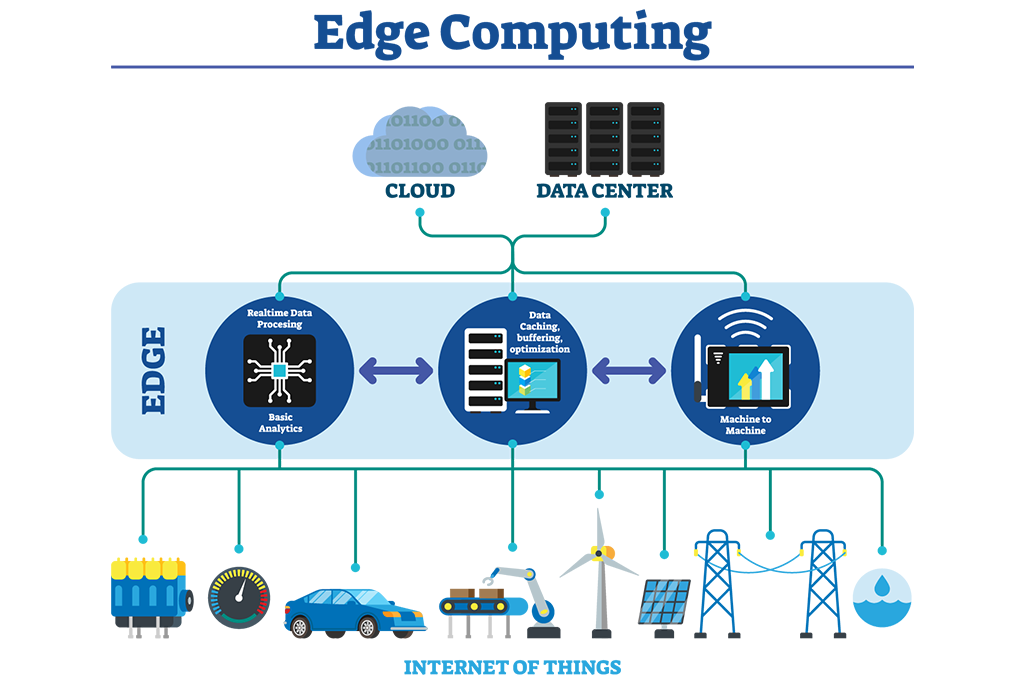
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the edge of the network, where data is generated. This approach differs from traditional cloud computing, where data is processed and stored in remote data centers, far from the edge of the network. With edge computing, data can be processed in real time, reducing the latency and improving the efficiency of data processing.
Edge Computing VS Traditional Cloud Computing
Edge computing and traditional cloud computing are two different approaches to data processing and storage, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Traditional cloud computing refers to the practice of using remote data centers to process and store data. This approach has been the dominant model for data processing and storage for many years, and it provides several benefits, such as low upfront costs, scalability, and high availability. However, traditional cloud computing also has its limitations, such as high latency and security concerns.
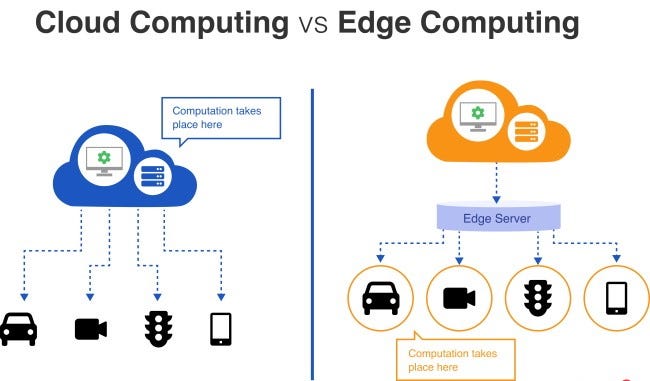
Edge computing, on the other hand, brings computation and data storage closer to the edge of the network, where data is generated. This approach reduces latency and improves the efficiency of data processing, making it ideal for real-time applications, such as augmented reality, robotics, and autonomous vehicles. Edge computing also enhances security and privacy by processing data locally, reducing the risk of data breaches, and ensuring that sensitive data is not transmitted over the network.
In conclusion, the choice between edge computing and traditional cloud computing depends on the specific requirements of the application. For applications that require real-time processing and low latency, edge computing may be the better choice, while for applications that prioritize scalability and cost-effectiveness, traditional cloud computing may be the better option.
Advantages of Edge Computing
- Reduced Latency: Edge computing reduces the latency of data processing, as data is processed closer to where it is generated. This is crucial in applications that require real-time processing, such as augmented reality, robotics, and autonomous vehicles.
- Improved Reliability: Edge computing eliminates the dependency on a central data center, reducing the risk of downtime in case of a failure in the central data center.
- Better Data Privacy: Edge computing enables data to be processed locally, reducing the risk of data privacy breaches and ensuring that sensitive data is not transmitted over the network.
- Cost-effectiveness: Edge computing reduces the cost of data processing by eliminating the need for expensive and power-hungry data centers.
Applications of Edge Computing
- Internet of Things (IoT): Edge computing is an ideal solution for IoT devices, as it enables data processing and analysis at the edge of the network, reducing the need for transmitting large amounts of data to the central data center.
- Automation and Robotics: Edge computing enables real-time data processing and decision-making for robots and automation systems, improving their efficiency and reliability.
- Healthcare: Edge computing can improve the efficiency of medical devices, such as wearable health monitoring devices, by processing and analyzing data at the edge of the network.
- Gaming: Edge computing can enhance the gaming experience by reducing latency and improving the quality of graphics and animations.
Conclusion
Edge computing is a growing trend in the field of computing, and it has the potential to revolutionize the way data is processed and analyzed. By bringing computation and data storage closer to the edge of the network, edge computing enables real-time data processing, reduces latency, and improves the efficiency of data processing. With the growing demand for low-latency and real-time data processing, edge computing is poised to become the future of data processing.
