WHAT IS CACHING ?
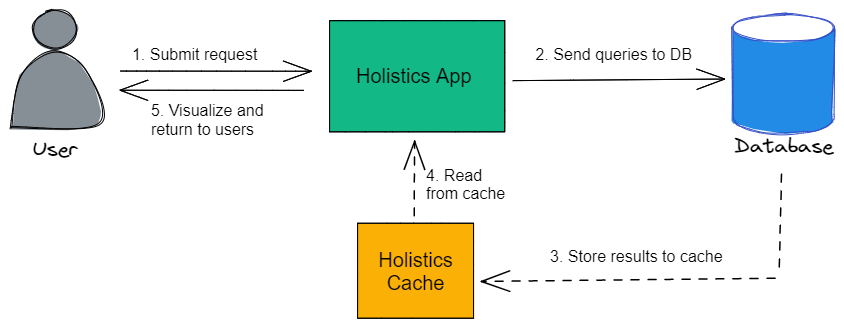
In simple terms, storing a subset of frequently accessed data, so we don’t have to fetch it again and again from the database, is called caching. It speeds up the process of accessing the data and also saves monetary cost.
WHEN TO USE CACHING ?
- When there is repetitive data return for same input.
- To improve latency among network layers
- When there is no or low volatility in data
- To reduce monetary cost
Caching in Spring Boot
To enable cache mechanism, first we need to add cache dependency in pom.xml of the Spring Boot application. It enables caching and configures a Cache Manager.
[POM Dependency]PROCESS OF CACHING
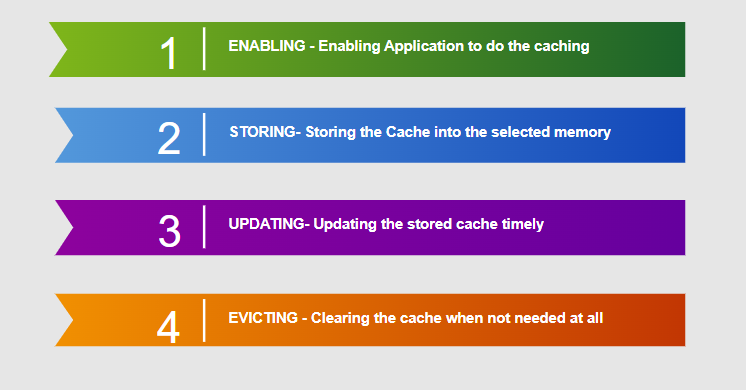
Now we will see how we can achieve the above process from Spring Boot.
1. Enabling The Cache
To enable caching, Spring Boot provides the annotation called Enable Caching. It is applied in top of main method of the application.
[Spring Boot] @SpringBootApplication @EnableCaching public static void main(String[] args){ } [Spring Boot]2. Storing In the Cache
@Cacheable is the annotation provided by the Spring Boot to know that which data should be stored in cache. We use this annotation on the method which will return the data to be stored.
[Spring Boot] @Cacheable(cacheNames=”name”, key=”#key”) public Data findData(args){ } [Spring Boot]We can provide many attributes in @Cacheable annotation like key, condition, cache names and sync.
Note : If we don’t provide the key in @Cacheable, Spring uses the default mechanism to create the key.
3. Updating The Cache
To update the created cache, we use the @CachePut annotation of Spring Boot. It supports all the attributes of
[Spring Boot] @Cacheable.@CachePut(cacheNames=”name”, key=”#key”) public Data updateData(args){ } [Spring Boot]Difference between @Cacheable and @CachePut is that, @Cacheable skips the method execution and @CachePut runs the method and put the result in cache.
Note : @Cacheable and @CachePut both can be used with same method but is not recommended, result may not match the expected result
4. Evicting The Cache
Evicting simply means deleting the cache information. We can delete all entries of a cache or can select a particular entry to be deleted using @CacheEvict annotation.
[Spring Boot] @CacheEvict(cacheNames=”name”, allEntries=true) public void(args){ } [Spring Boot]We use above-mentioned annotations for caching in spring boot, but there are many other annotations available.
You may refer to the official documentation of spring for more information.
References
Cache Definition and Explanation – KeyCDN Support
In computing, cache is a widely used method for storing information so that it can be later accessed much more quickly…www.keycdn.com
Caching
The Spring Framework provides support for transparently adding caching to an application. At its core, the abstraction…docs.spring.io
